Scrum Practice
Scrum Practice: Artifacts
Scrum artifacts capture the work that needs to be done, what the team is working on now, and the results of that work. They make progress visible and keep everyone aligned. The three main artifacts are the Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment.
| Term | Description | Tools Used in TDM |
|---|---|---|
Product Backlog (a) |
A big list of everything the team might need to build for the project, like a to-do list of features and ideas (Product Goal). |
|
Sprint Backlog (b) |
A smaller list taken from the Product Backlog that the team chooses and commits to work on during the current sprint (Sprint Goal). |
|
Increment (c) |
The working product or feature that comes out of a sprint — something usable and potentially releasable (Definition of Done). |
|
To support these artifacts in practice, projects rely on tools that help capture, track, and share progress throughout the sprint. The next section defines the tools used in TDM.
Tools Used in TDM
In TDM tools such as Kanban board (MS Planner), MS Teams, and GitHub play a central role in supporting Scrum artifacts and ensuring effective project delivery.
Kanban Board (Progress Tracking)
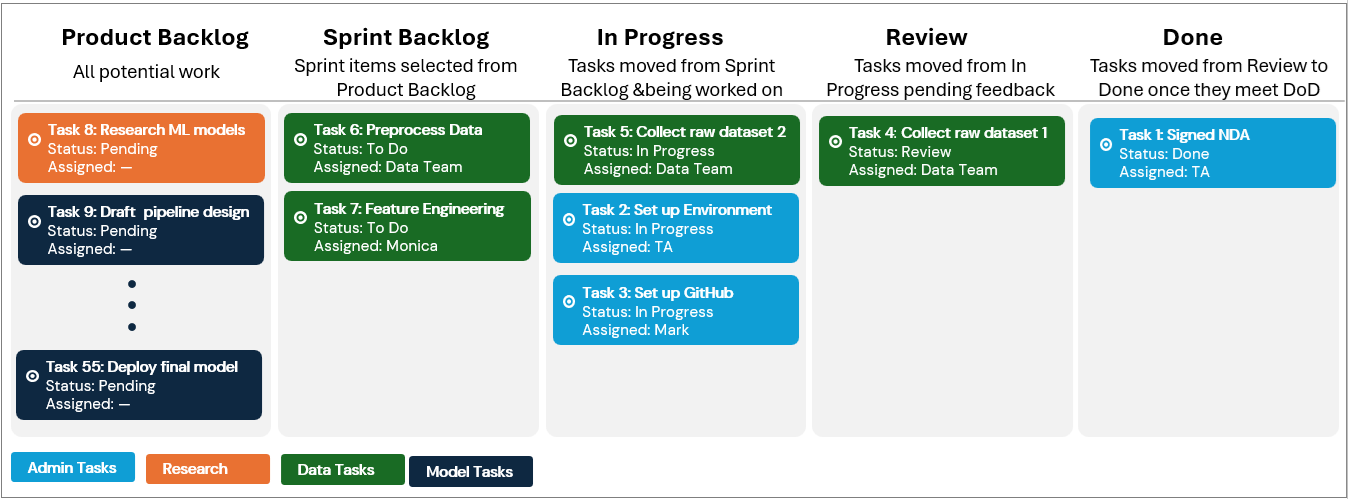
A Kanban board helps teams visualize work, track progress, and stay transparent. It highlights what’s pending, in progress, and completed. In TDM, we use MS Planner integrated with the project’s MS Teams channel.
Below is a sample board with different task types (admin, research, data, model) across workflow stages. Typically, the Product Backlog is managed by the mentor (Product Owner) and TA (Scrum Master), the Sprint Backlog is maintained by the TA and students (Development Team), tasks in In Progress are owned by the students, work in Review is checked by the mentor, and tasks in Done are confirmed together by the students and mentor.
To support this workflow, teams in TDM use MS Teams.
MS Teams (Communication and Collaboration)
MS Teams helps the team stay connected, share updates, and collaborate in one place. It supports communication, makes collaboration easier, and keeps everyone aligned. In TDM, we use the MS Teams project channel as the central hub for all project activities. That’s why it is important to review the guidelines below and follow them consistently throughout the project term.
| Role | Guidelines |
|---|---|
Team Members |
|
TA |
|
GitHub (Code Collaboration)
GitHub helps teams manage code, track changes, and review work. It keeps versions organized and supports smooth collaboration.
In TDM, each project typically gets a dedicated repository within the TDM GitHub account. However, if security or compliance requirements mandate that the project remain within the corporate partner’s environment, the relevant setup is conducted there.
Scrum Artifacts Cartoon

Cartoon illustrated by Marija Hajnal